Outline
Visible Light is the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum — a spectrum that also includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared and ultraviolet radiations, X-rays, and gamma rays.
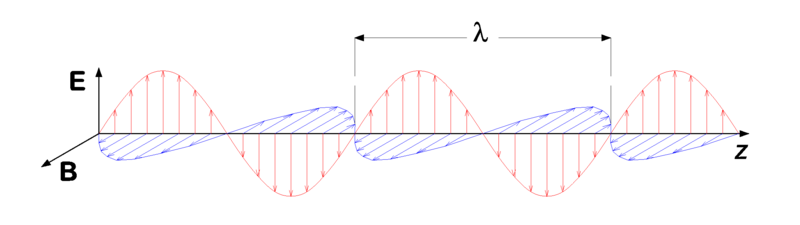
Electromagnetic waves can be modelled as a transverse wave that can travel through a vacuum.
The E axis is the electric field, the B the magnetic field.
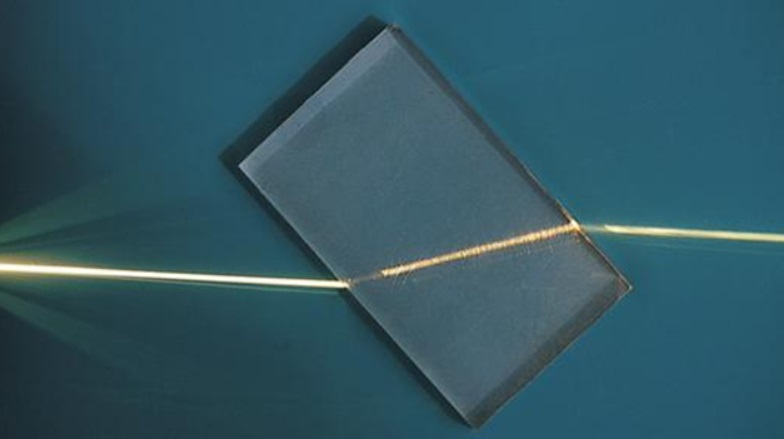
Refraction is the change in direction of propagation of a wave as its speed changes.
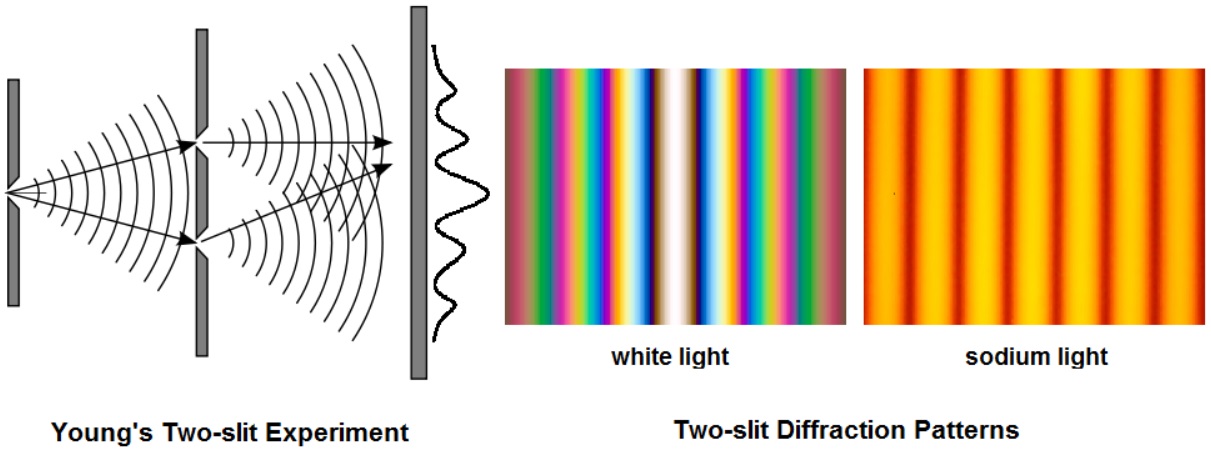
Diffraction is the bending/spreading of waves as they pass through an aperture or past a sharp edge.
The plane of polarisation of an electromagnetic wave is the plane defined by the direction of travel and the oscillating electric field.
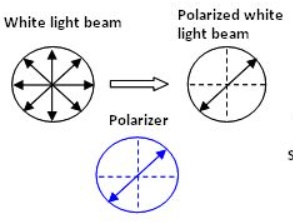
Lectures
Videos
Light Is Waves: Crash Course Physics #39
What the heck is light, Science Asylum
Light: Crash Course Astronomy #24
What is Light? Maxwell and the Electromagnetic Spectrum, Profeesor Dave
Why does light bend when it enters glass?, Fermilab
Why does light slow down in water?
Polarization of light, linear and circular | Light waves | Physics | Khan Academy
How Do Polarized Sunglasses Work?!, Science Asylum
|


