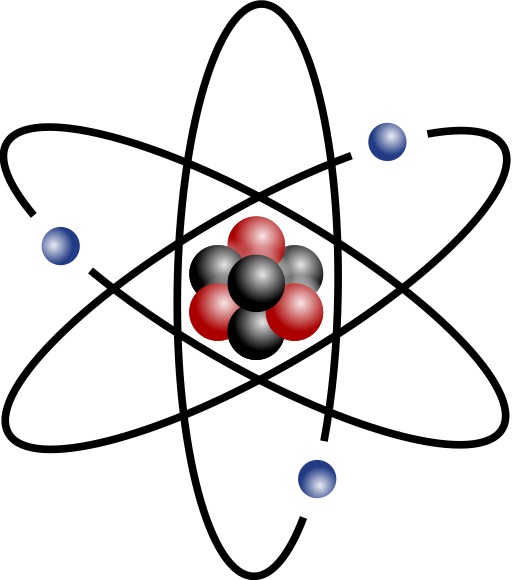
Key Ideas
Atoms contain positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons.
Remember your year 9 and 10 atomic structure
- The Nucleus of an atom is made up of Protons and Neutrons
- The number of protons defines what element the atom is; Carbon has 6 Protons, any atom with 6 Protons is Carbon
- Protons are positively charged (we say they have a charge of +1)
- Electrons sit in 'orbits', 'shells' or 'energy levels' around the Nucleus
- Electrons are negatively charged (we say they have a charge of -1)
- An Atom has a neutral charge (equal numbers of Protons and Electrons)
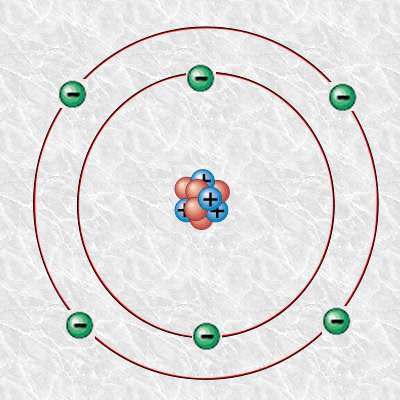
Carbon Atom (6 Protons, 6 Neutrons and 6 Electrons in 2 electron shells)
Image courtesy of Alejandro Porto
Atoms become charged when electrons are transferred from one object to another or redistributed on one object.
Note; Protons are not 'shared' in the way Electrons can be shared or moved. If an Atom loses (or gains) a Proton, it has changed what Element it is.
Protons are tightly bound in the Nucleus and do not move. However, positive ions (atoms that are missing electrons) may move in solution. For example
dissolved salt (NaCl) will separate into Na+ and Cl- ions when dissolved in water (H2O) and negatively charged objects
can be used to attract the positive Ions. This can be seen as the movement of positive charge (which it is), however, it is not the movement of Protons,
it is the movement of postively charged Atoms or Molecules (Ions).
Electrostatics is the study of charges at rest (or more particularly, the interaction between charges or charged objects), rather than the
movement of charge.
Two like charges exert repulsive forces on each other, whereas two opposite charges exert attractive forces on each other.
The force between the two objects can be calculated using Coulomb's Law
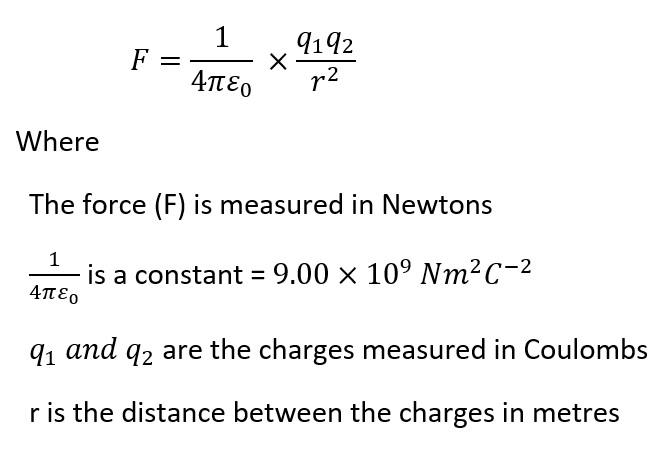
- Note, if the charges are opposite charges (+ and -) then the force will be negative. Thus, an attractive force has a negative sign
- And so, if the charges are the same charges (+ and + or - and -) then the force will be positive. Thus, a repulsive force has a postive sign
Insulators, conductors and semi-conductors
Importantly, insulators and conductors sit on a continuum. There is no such thing as a perfect insulator or conductor. Given enough Potential Difference
(difference in the voltage) between the two ends of an insulator, electrical current will flow.
Insulator (Electrical) a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which
cannot readily move.
Conductor (Electrical) a material that allows the flow of charge (usually by the free movement of Electrons).
Semi-conductor a material that has some level of conductivity, usually its conductivity rises with temperature rise.
Electrical Potential Energy
As you know, gravity makes a pen fall when you let it go and we can calculate the pen's potential energy at any point in its fall. The attraction of two opposite
charges can be compared to gravity, and calculations of Electrical Potential Energy can be made.
Energy is required to separate positive and negative charges and this charge separation produces an electrical potential difference that
can be used to drive current in circuits.
For example, the different charges (voltages) in a battery 'pull' electrons from the negative end to the positive end.
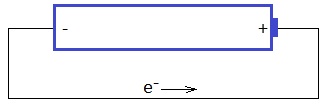
Two important points
conventional current, we define the flow of 'conventional current', as electrical current flowing from the positive to the negative end of any circuit. This
is the opposite to what actually happens (Electrons flow toward the positive end of a circuit).
voltage (Electrical Potential) is defined as the Force required, per unit of charge, to move a charge a distance.
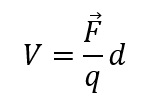 In an electrical circuit voltage is measured using a voltmeter.
In an electrical circuit voltage is measured using a voltmeter.
Click here for more details on voltage
Two key electrical circuit devices
- Fuses or Circuit Breakers
A fuse is an 'over current' cut out device. They are specifically designed to work within a maximum current range. When that range is exceeded, they quickly heat up
and melt, thus breaking the contact. Once a fuse has broken it must be replaced.
Circuit breakers come in a number of variations. A common form uses a bimetal strip that is designed such that when the operating current is exceeded, it
heats up and bends, moving it away from the 'contact' and thus breaking the circuit.
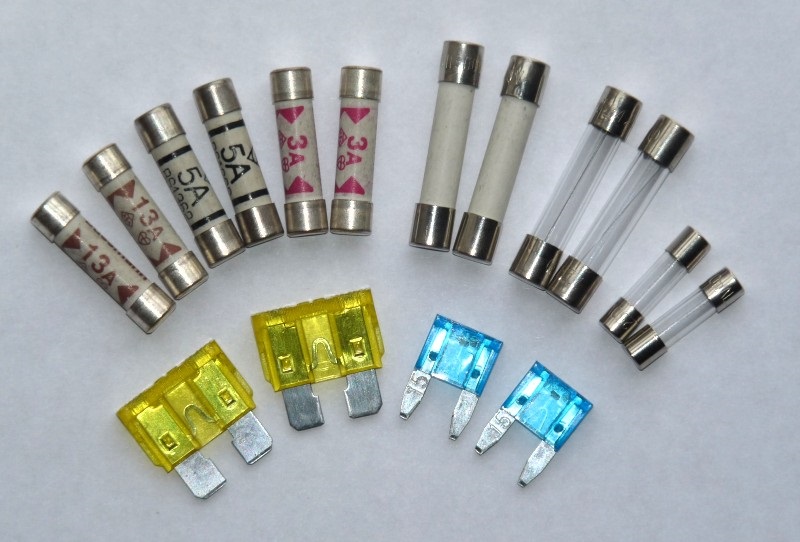
 
Image courtesy Pfnicholls Image courtesy of Dmitry G
- Residual Current Devices (RCD)
RCDs compare the 'supply' and 'return' sides of an electrical current and immediately break the circuit if the two are different. The difference would generally occur
if there is a 'leakage' from the circuit.

Image courtesy of User-2000
Electric current is carried by discrete charge carriers (Electrons). Current can hence only be a multiple of the charge of an Electron. Charge is conserved at all points in an electrical circuit.
Electric current is the rate of flow of charge.
Lectures
Lecture - Potential difference and electric current
Videos
Science Asylum, What does an Atom really look like
SciShow, This is not what an Atom looks like
Minute Physics, A better way to picture atoms
SciShow, Ben Franklin (why current flows the wrong way)
Crash Course, Electric Charge and Coulombs Law
Don't memorise, What is an elctrical fuse
WorkSafeQLD, Busting Myths Circuit breakers and fuses
|